- Smart contract: A digital agreement, but without the need for lawyers, banks, or any middleman. Once the conditions in the contract are fulfilled, the contract executes itself. .
- Atomic swap protocol: It enables Peer-to-Peer (P2P) transactions between parties wishing to exchange cryptocurrencies on different blockchain networks. .
- Cryptographic hashing algorithm: A mathematical function that converts data into a code, used to securely verify and protect information. .
- Flash loan: An instant, no-collateral loan in crypto that must be borrowed and fully repaid within a single blockchain transaction. .
Trading cryptocurrencies usually involves using a centralized exchange, like Binance or Coinbase. These platforms help people buy and sell coins, but they also control the process and hold users’ funds during the trade. This can lead to higher fees, slower transactions, and security risks if the exchange gets hacked or shuts down.
This is where atomic swaps come in. Atomic swaps allow two people to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other — even if the coins are on different blockchains. The process is powered by smart contracts and cryptography, making it secure and automatic. There’s no need for a bank, exchange, or any middleman.
In this article, you’ll learn how atomic swaps work, their key benefits, and some drawbacks that still exist today. Whether you’re new to crypto or just curious about decentralized trading, this guide will help you understand the basics in simple terms.
How Do Atomic Swaps Work?
Atomic swaps allow two parties to securely exchange cryptocurrencies across different blockchains without needing a central exchange. These swaps rely on cryptographic techniques and a special type of smart contract called a Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC), which ensures that the exchange is fair and trustless.
HTLC is a special type of smart contract used to make sure that users can safely trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other, without needing to trust each other or use a third party.
The contract locks the money with a secret code called “hash”, and the money can only be unlocked if the correct code is used before a set time. If no one uses the correct code in time, the money goes back to the sender.
It’s crucial for atomic swaps, because simply users can be sure that they will either both get what they agreed on, or both get their money back. This helps prevent cheating and keeps the swap fair and secure.
The smart contract acts like a virtual vault, ensuring that both sides follow the agreed terms. Here’s how the process works:
- Step 1: The first party deposits their cryptocurrency into a locked contract address within the vault.
- Step 2: The second party verifies the deposit, then sends their own cryptocurrency to a separate locked contract address.
- Step 3: The smart contract checks that both parties have locked their assets according to the agreed terms.
- Step 4: Once verified, the contract automatically releases the funds to each party.
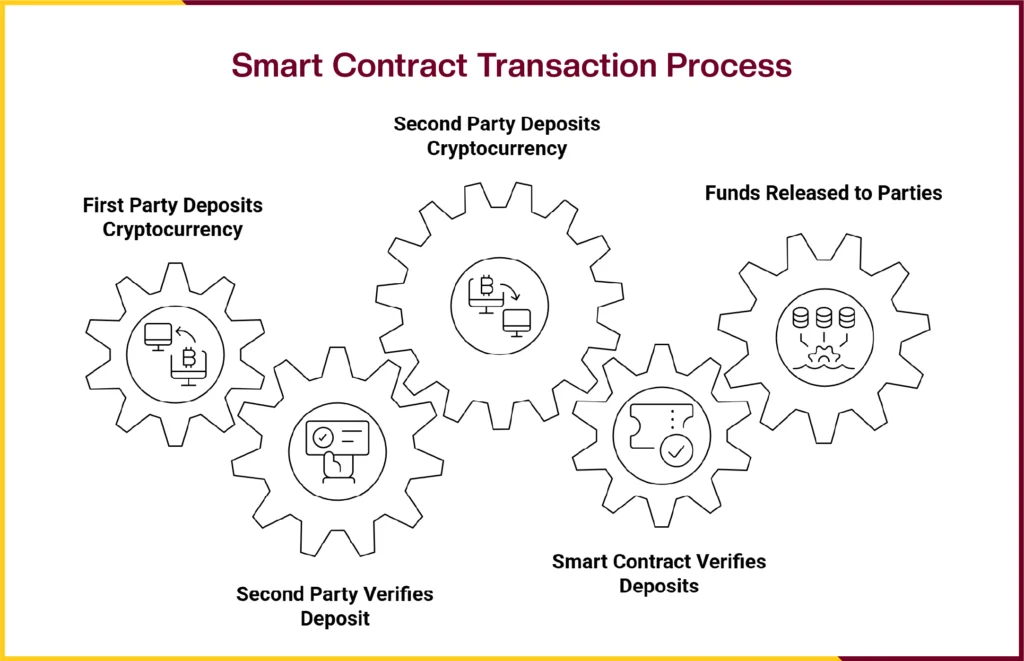
If either party fails to fulfill their part of the agreement, the swap is automatically canceled. In such cases, any cryptocurrency already sent is refunded to its original sender.
Benefits of Atomic Swaps
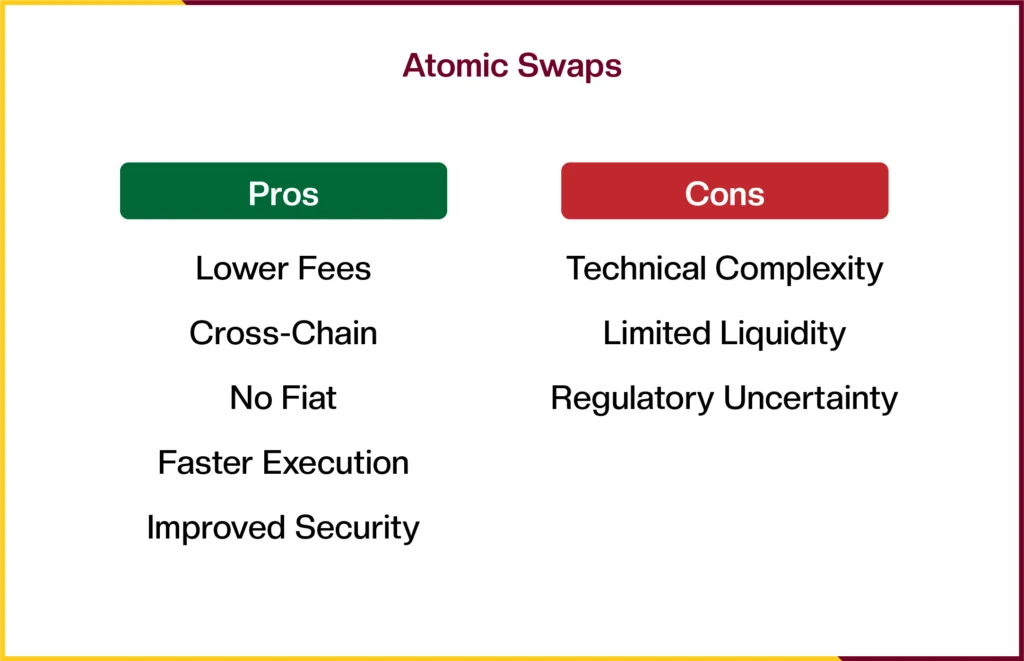
Atomic swaps offer several advantages for crypto traders, especially when exchanging assets across different blockchains:
- Lower Fees: By eliminating intermediaries, users avoid extra costs typically charged by centralized exchanges.
- Cross-Chain Compatibility: Traders can swap cryptocurrencies across different blockchains without exposing their private keys or assets.
- No Fiat Involvement: Swaps are entirely crypto-to-crypto, removing the need for fiat currencies as an intermediary or valuation baseline.
- Faster Execution: Once both parties meet the agreed conditions, the smart contract triggers the swap automatically, enabling quick and efficient transactions.
- Improved Security: The use of smart contracts ensures that funds are only exchanged if both sides comply with the terms. If one party fails, the other retains their assets, minimizing risk.
Downsides of Atomic Swaps
While atomic swaps offer powerful benefits, they still come with a few important challenges. One major issue is the technical complexity involved. Atomic swaps use HTLC, so If one party doesn’t follow through, both get their funds back automatically.
Another limitation is that only certain cryptocurrencies can be used, since atomic swaps require both coins to share a similar cryptographic hashing algorithm. This restricts the number of supported networks and reduces trading flexibility.
For example, Litecoin, Decred, and Komodo support atomic swaps because they use compatible hashing and scripting functions. On the other hand, Bitcoin does not natively support atomic swaps, and many other blockchains also lack the required features.
Finally, the process itself is more complicated than using a regular centralized exchange, with multiple steps that can be confusing or time-consuming for everyday users.
Flash Loans: Instant Loans with Atomic Logic
Another exciting use of atomic technology in crypto is something called a flash loan. A flash loan is a special kind of loan in the world of decentralized finance (DeFi). It lets someone borrow a large amount of cryptocurrency without any collateral, but for a very short time.
The borrower usually takes a loan, uses it for trading or investment, and repays it all in the same blockchain transaction. If they don’t repay the full amount plus interest, the entire transaction is automatically canceled, and it’s like the loan never happened.
This is possible because flash loans use the same atomic principles as atomic swaps. Everything must be done in one go, or nothing happens at all. This protects both sides, the lender doesn’t lose money, and the borrower doesn’t face long-term debt.
Flash loans are often used by advanced traders to take advantage of quick price changes in the market.
For example, someone might borrow money, buy a coin at a low price on one exchange, sell it for a higher price on another, repay the loan, and keep the profit, all within seconds.
What are the currencies that support atomic swaps?
Not all cryptocurrencies support atomic swaps, but some popular ones do. Litecoin, Decred, and Komodo were among the first to use this technology. Other coins like Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash, and Zcash have also added support through special upgrades or second-layer solutions.
Bitcoin does not support atomic swaps in its basic form, Instead, it needs extra tools like the Lightning Network to make it work properly. This is because atomic swaps need special features like smart contracts and timelocks, which are limited on Bitcoin’s main blockchain. So while Bitcoin can be used in atomic swaps, it often needs help from other systems to do it smoothly.
While powerful, flash loans are also risky and technical. They are mostly used by experienced users who understand smart contracts and how blockchain systems work.
Atomic swaps and flash loans show how powerful and flexible blockchain technology can be. They give users more control, faster transactions, and new ways to trade or borrow without relying on traditional systems. While these tools are still evolving and can be complex, they open the door to a more open and decentralized financial world.







